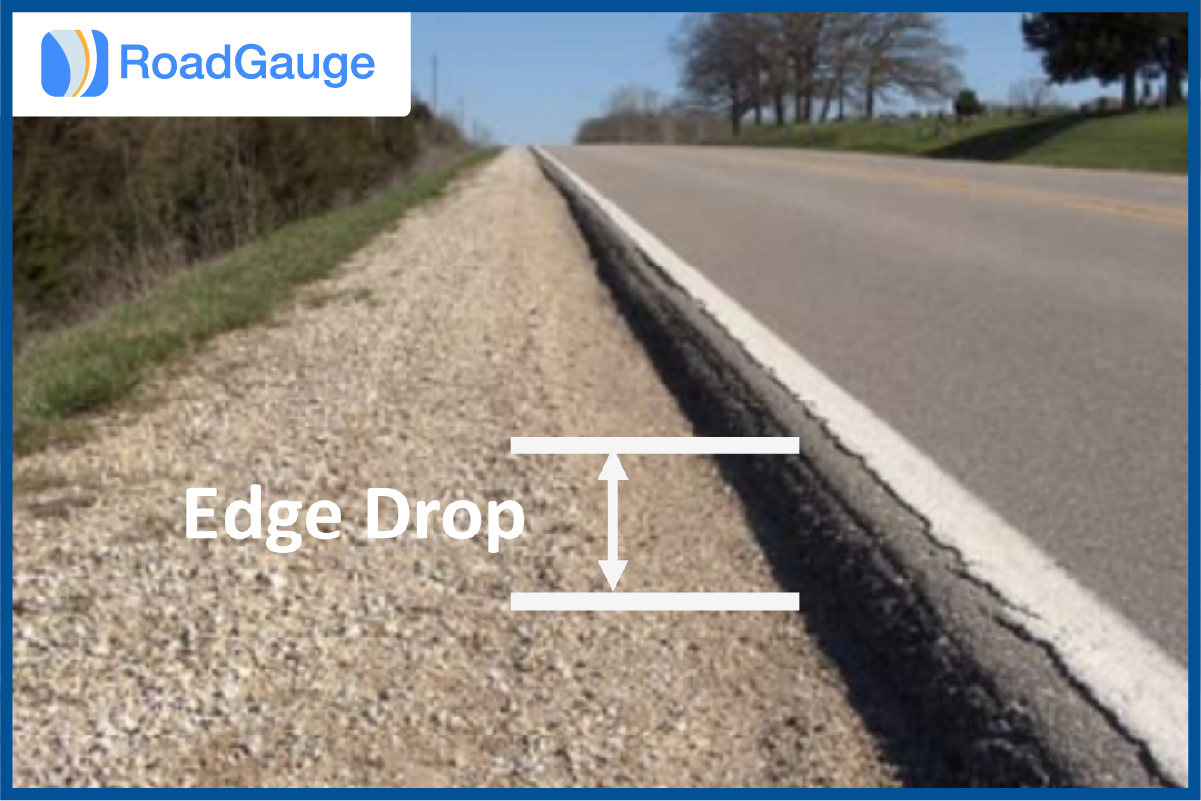

Edge drops, or edge drop-offs, refer to sudden height differences between the edge of a paved road and the adjacent unpaved shoulder. These occur due to various factors, such as erosion from rainwater runoff, which washes away shoulder material and heavy traffic that compacts or displaces the soil. Road resurfacing projects can also create edge drops if the increased pavement height isn’t matched with proper shoulder adjustments. Inadequate or infrequent maintenance often worsens these conditions, making edge drops a common issue, especially on rural or high-traffic roads where environmental factors accelerate deterioration.
The safety risks associated with edge drops are significant. When a vehicle veers off the pavement, the height difference can make it difficult to regain control, increasing the likelihood of crashes or rollovers. This risk is particularly high for motorcyclists and in situations with poor visibility, such as nighttime driving or adverse weather conditions. These hazards highlight the danger posed by uneven transitions between road surfaces and shoulders.
Detecting and measuring edge drops in roads involves several methods such as visual inspection to identify noticeable elevation changes between the pavement and adjacent areas. Straightedges and leveling devices precisely measure height differences, while advanced tools like laser profilometers and 3D surface mapping deliver highly accurate assessments across large road areas. High-speed systems, such as rolling straightedges and optical sensors, continuously monitor highways. Specialized software analyzes the collected data to evaluate severity and prioritize maintenance, improving road safety.
RoadGaugeAI, our innovative web-based software, transforms edge drop measurement with unmatched precision. Using traffic-speed videos from standard consumer cameras like GoPro, it delivers millimeter-level accuracy. Want to learn more? Reach out at info@roadgauge.ai or visit our contact page.

